Scalp hair cortisol and testosterone levels in patients with sarcoidosis.
Patients with sarcoidosis usually expertise fatigue and psychological misery, however little is thought concerning the etiology of those situations. While serum and saliva steroid hormones are used to observe acute steroid levels, scalp hair evaluation is a comparatively new methodology enabling measurement of long-term steroid levels, together with hair cortisol reflecting continual stress.
We investigated whether or not scalp hair cortisol and testosterone levels differ between sarcoidosis patients each with and with out fatigue and normal inhabitants controls. Additionally, we studied if these hormones may function goal biomarkers for psychological misery in patients with sarcoidosis.
We measured hair steroid levels utilizing liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in glucocorticoid naïve sarcoidosis patients. Patients accomplished the Perceived Stress Scale, Fatigue Assessment Scale, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and Short Form 36 (SF-36). Hair steroid levels from 293 individuals of the population-based Lifelines cohort examine served as controls.
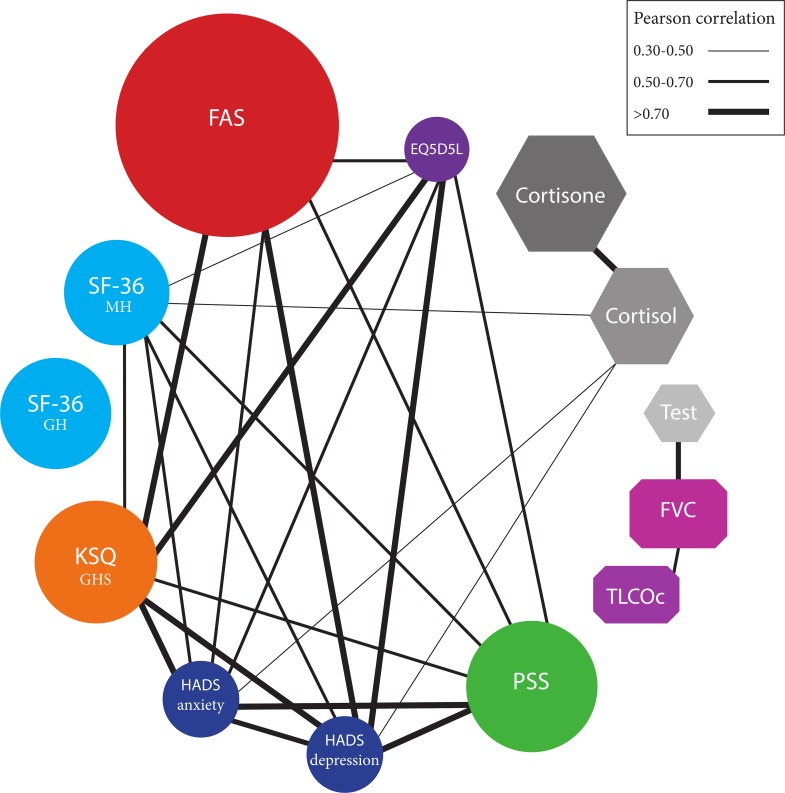
Thirty-two patients (14 males) had been included. Hair cortisol, however not testosterone, concentrations had been considerably larger in patients with sarcoidosis than in normal inhabitants controls (imply 6.6 versus 2.7 pg/mg, p<0.001).
No variations had been discovered in hair cortisol and testosterone levels between fatigued and non-fatigued patients with sarcoidosis. Hair cortisol of sarcoidosis patients correlated considerably with nervousness (r = 0.47, p = 0.01), despair (r = 0.46, p = 0.01), and SF-36 psychological area (r = -0.38, p = 0.03), however not with fatigue.Patients with sarcoidosis have chronically larger levels of the stress hormone cortisol than the traditional inhabitants, whereas testosterone levels in hair didn’t differ.
Hair cortisol levels had been positively associated to subjective measures of psychological misery, however to not fatigue. Our examine reveals that hair cortisol is a promising non-invasive biomarker for psychological misery in patients with sarcoidosis.ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03108547. Registered 31 March 2017, retrospectively registered.
BACKGROUND
Theory and analysis counsel that generalized nervousness dysfunction (GAD) is related with diminished high quality of life and restriction in valued motion. The goal of this examine was to look at the relevance of values-consistent habits (valued motion) in understanding the impairment in high quality of life in GAD.METHOD
STreatment-seeking shoppers with a principal prognosis of GAD (n = 30) had been in contrast with demographically matched nonanxious controls (n = 30) utilizing self-report measures.RESULTSParticipants with GAD reported considerably much less valued motion in contrast with controls, and inside the GAD group, diminished valued motion was not absolutely defined by despair comorbidity. Valued motion was considerably correlated with measures of experiential avoidance, misery about feelings, and high quality of life. Further, constant with a theoretical mannequin of GAD, restrictions in valued motion contributed distinctive variance to diminished high quality of life over and above the contributions of gender, GAD severity, experiential avoidance, misery about feelings, and despair comorbidity.
Finally, an acceptance-based behavioral remedy considerably improved self-reports of valued motion for GAD shoppers with 40% attaining clinically vital change in this area.CONCLUSIONSThe findings present preliminary help for the relevance of valued motion in understanding the useful impairment related with GAD, and the useful results of an acceptance-based habits remedy in rising valued motion.
OBJECTIVET
o use the Short Form 36 (SF-36) to find out the extent to which health-related high quality of life (HRQOL) is decreased amongst main caregivers of patients with cerebrovascular accident (CVA) or diabetes mellitus (DM) in comparison with regular Taiwanese inhabitants and to establish the determinants of this lower.
METHODSData from a cross-sectional survey of 187 main caregivers who had accountability for inpatients with a medically verified prognosis of CVA or DM had been in comparison with these of randomly chosen residents. Data had been collected by face-to-face interviews with skilled interviewers.RESULTS.
The age- and gender-adjusted imply variations of caregivers on primarily psychological scales of SF-36 had been considerably unfavourable in comparison with normal inhabitants, as a lot as a 3-12 factors discount on this 100-point scale. While the age- and gender-adjusted imply variations on bodily functioning and bodily ache scales had been considerably optimistic, as a lot as a 3-6 factors enhance.
Effects of caregiving on the perceived social lifetime of the caregiver and incapacity of inpatients in consuming and getting in/away from bed had been related with the SF-36 Physical Component Scale (PCS) rating whereas feminine gender, kind of caregiver, care conflicts, diploma of care demand of every day dwelling, and results of caregivering on perceived social lifetime of caregivers had been negatively related with the SF-36 Mental Component Scale (MCS) rating.
CONCLUSIONSPrimary caregivers of CVA or DM hospitalized aged have poorer psychological however higher bodily well-being than the inhabitants norm. Both caregiver and inpatient components contribute to caregivers’ HRQOL.